Scientists Prepared a New Kind of Stretchable Conductor based on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Films
Date:27-11-2012 Print
Stretchable conductors, remaining conductive under tensile strains, are essential to realize stretchable electronics. Two conceptually distinct, but complementary, methods are concurrently being adopted to obtain stretchable conductors: one relies on the unconventional structures of traditional materials; the other is to exploit novel materials, including carbon nanotube, graphene and polymers. By virtue of their 1D attributes and intrinsically high strength and conductivity, carbon nanotubes are ideal candidates to prepare stretchable conductors.
Recently, the group of Nanomaterials and Mesoscopic Physics (Group A05) at the Laboratory for Advanced Materials & Structure Analysis, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported some creative results on the applications of single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) films in stretchable electronics. CAI Le, a PhD candidate under the supervision of Prof. XIE Sishen, prepared a kind of stretchable conductor by embedding the SWCNT films in polymer elastomer and demonstrated the utility of this stretchable conductor as connecting wires in stretchable circuits.
Polymer embedment, avoiding dispersant agent and ultrasonic treatment, is a simple and environmental-friendly method, which is well suitable for directly synthesized SWCNT films. The as-prepared stretchable conductors possess excellent transparency, conductivity and stretchability—the transmittance in visible region reaches 60% while the sheet resistance is as low as dozens of Ohms, and high conductivity is maintained under repetitively stretching to a tensile strain as high as 50%. The introduction of PDMS matrix can effectively mitigate the stress concentration and maintain the electrical integration of SWCNT films, which, along with the 1D attributes of carbon nanotubes, results in the aforementioned superior stretchability. Owing to the high transparency and stretchability, the reported stretchable conductors will be widely used not only as interconnects but also as electrodes for many intelligent electronics, such as stretchable energy storage devices, optoelectronic devices and so on. The results are published in Advanced Functional Materials (DOI:10.1002/adfm.201201013).
The reported work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Ministry of Science and Technology, Beijing Municipal Education Commission.
Link to the paper: Highly Transparent and Conductive Stretchable Conductors Based on Hierarchical Reticulate Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Architecture.pdf
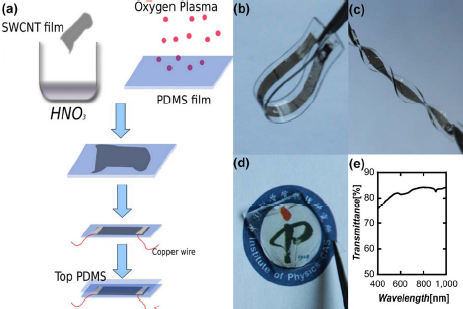 |
| Figure 1. (a) Schematic illustration of the procedures to prepare SWCNT/PDMS stretchable conductors. (b,c) Photographs of a bended and twisted SWCNT/PDMS stretchable conductor, showing their flexibility. (d) Photograph of a transparent SWCNT/PDMS film. (e) The transmittance spectra of the SWCNT/PDMS film shown in d).(Image by CAI Le et al) |
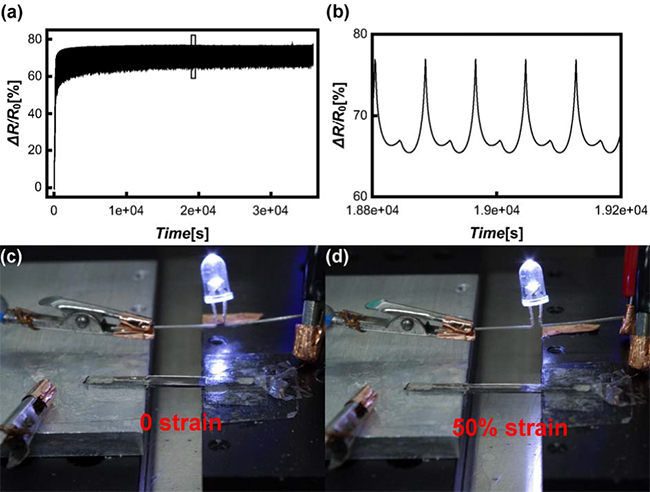 |
| Figure 2. a) ΔR/R0 curve in about 500 cycles of stretching and releasing with a strain of 40%. b) Details of four stable cycles (Enlargements of the parts enclosed in the rectangle in a)). c) and d) Photographs of a LED illuminated using a SWCNT/PDMS strip as connecting wire, where the strain applied to the strip is 0 and 50%, respectively. (Image by CAI Le et al) |