A Hexagonal Oxide Film that Can Act as a Water-Soluble Sacrificial Layer for Membrane Freestanding
Date:20-01-2026 Print
Functional oxide membranes, with a freestanding form, have many potential applications in flexible devices. To date, however, the realized materials have been limited to perovskite structural systems.
Here, Prof. LU Nianpeng's groups from Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, synthesized a new hexagonal BaAl₂O₄ film, which can nicely overcome these limitations.
First, the BaAl₂O₄ film can dissolve rapidly in water within a sub-minute, yet remains highly stable against air, oxygen, and ammonia, even at high temperatures. This unusual combination of fast water solubility and exceptional thermal and chemical stability allows both in-situ and ex-situ growth of high-quality functional films.
Second, it is a hexagonal structure that is greatly different from the previously reported cubic or tetragonal materials, which can be widely used to exfoliate the six-fold and three-fold symmetric films.
By using this hexagonal BaAl₂O₄ as a water-soluble sacrificial layer, the research team have successfully fabricated a broad range of freestanding membranes, including the multiferroic material YMnO₃, lithium-ion battery cathode LiCoO₂, antiferromagnetic oxide α-Fe₂O₃, field effect channel material In₂O₃, typical p-type semiconductor NiO, ultra-wide bandgap semiconductor β-Ga₂O₃, and superconducting nitride TiN.
Moreover, during the film growth, they find a unique interfacial strain relaxation mechanism between the films and substrate, which guarantees the high-crystallinity of grown films and corresponding freestanding membranes.
The device application is illustrated by the wide bandgap semiconductor β-Ga₂O₃ membranes. The fabricated flexible solar-blind photodetectors from the high-quality β-Ga₂O₃ membranes exhibit high performance and excellent mechanical flexibility, which achieves a large photo-to-dark current ratio (10⁴) and a very high detection responsivity (3.79×10³ mA/W).
This work entitled "Water-soluble hexagonal BaAl₂O₄ as sacrificial layer for freestanding crystalline membranes and flexible devices" was published on Nature Materials. Link for the article: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-026-02486-w.
This study was supported by the CAS Project for Young Scientists in Basic Research, the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Beijing Nature Science Foundation. PhD candidate students LI Mengcheng and LU Chao are the first coauthors. Prof. ZHANG Qinghua from Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Prof. LI Peigang from the Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications provide great help during the study.
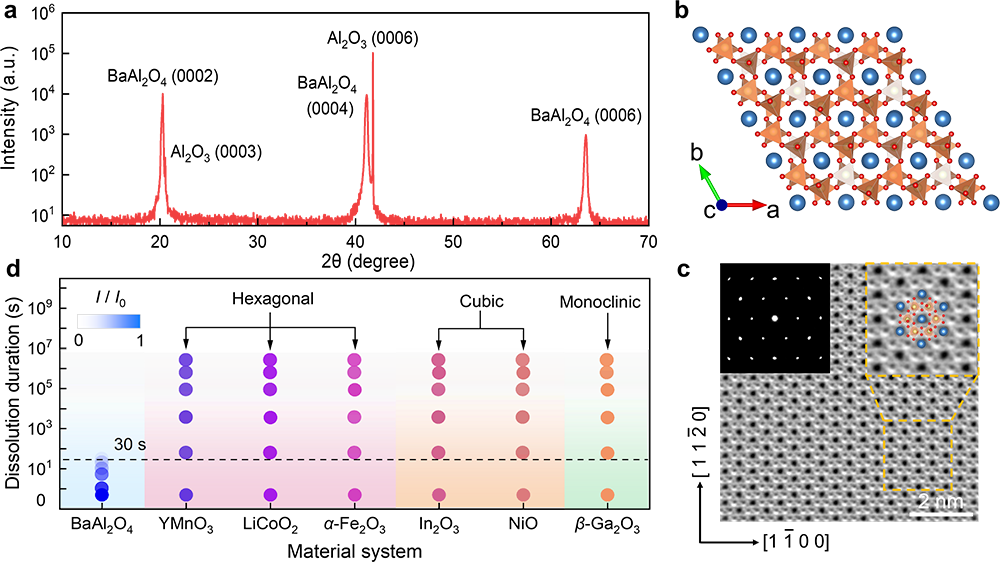
Fig.1 Synthesized hexagonal BaAl₂O₄ film as a water-soluble sacrificial layer. (Image by Institute of Physics)
Contact:
Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
LU Nianpeng
Email: lunianpeng@iphy.ac.cn
Key words:
Hexagonal BaAl₂O₄ film; Water-soluble sacrificial layer; Freestanding membrane; Flexible device
Abstract:
Freestanding membranes of hexagonal oxides remain difficult to obtain. In this work, a water-soluble crystalline hexagonal BaAl₂O₄ is found to serve as a sacrificial layer for obtaining freestanding membranes with 6-fold or 3-fold symmetry.